Last updated on March 13th, 2025 at 10:43 am
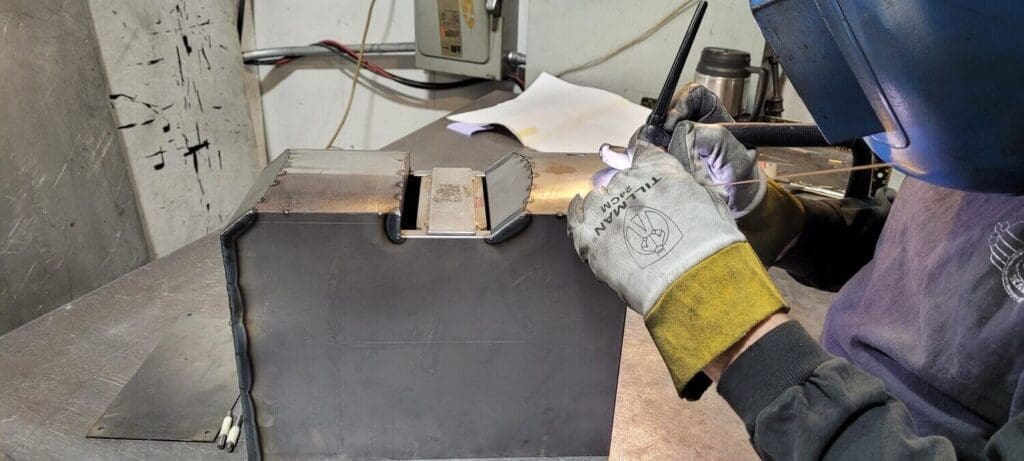
Sheet metal fabrication often involves assembling separate components into a single part.

We excel in high-quality welding at Approved Sheet Metal. But it’s not the only assembly method we offer at our Hudson, NH shop. Our team also specializes in welding alternatives like rivets and metal fasteners.
Curious which assembly method is right for your part? Here are several use cases to guide you in the right direction.
Table of Contents
- 1 Welding vs. Fastening for Sheet Metal Fabrication
- 1.0.1 Use case #1: Designing a sheet metal fabrication quickly and easily.
- 1.0.2 Use case #2: Adding strength and durability to a sheet metal fabrication.
- 1.0.3 Use case #3: Taking apart and reattaching assemblies.
- 1.0.4 Use case #4: Making a sheet metal fabrication watertight.
- 1.0.5 Use case #5: Achieving a clean, never-there seam.
- 1.0.6 Use case #6: Breaking down a box into different pieces.
- 2 Post-Processing & Maintenance Implications
- 3 Sheet Metal Part Design for Manufacturing Tip
- 4 Welding Vs Fastening FAQ
- 4.0.1 What are the main assembly methods for sheet metal fabrication?
- 4.0.2 When should I choose welding over fastening for my sheet metal fabrication project?
- 4.0.3 What are the advantages of using fasteners in sheet metal fabrication?
- 4.0.4 How do I decide between welding and fastening for my specific project?
- 4.0.5 Which assembly method is more cost-effective, welding, or fastening?
Welding vs. Fastening for Sheet Metal Fabrication
Use case #1: Designing a sheet metal fabrication quickly and easily.
Welding is easier to incorporate into a design than fastening. When using fasteners, engineers must consider factors such as overlapping flanges and hardware selection. If you need a relatively simple part fabricated quickly and easily, welding is probably your best option.
Use case #2: Adding strength and durability to a sheet metal fabrication.
In addition to holding parts together, fasteners add strength and durability to a part. Rivnuts, for example, add strong load-bearing threads to thin or weak sheet metal parts, making them more resilient to pressure.
Use case #3: Taking apart and reattaching assemblies.
Welding creates a permanent joint, while fasteners can be assembled and disassembled with ease. Applications like chassis, indoor and outdoor furniture, car dashboard attachments, bicycles, and solar panels are better suited for fasteners, which disassemble as needed.
Use case #4: Making a sheet metal fabrication watertight.
When a part needs to be watertight, welding is the obvious choice for preventing leaks. But not all welding methods provide airtight and watertight welds, so be sure to work with a shop that specializes in seam welding.
Use case #5: Achieving a clean, never-there seam.
If you need your sheet metal assembly to look like it was formed from one smooth sheet, welding is the best option. We can add a layer of powder coating or plating for a clean finish.
Use case #6: Breaking down a box into different pieces.
Even special tooling can’t always access deep boxes. In these cases, a deep box must be taken apart, formed, and
then reassembled. Both welding and fasteners work well for reassembling deep formed parts.
When it comes to cost, fasteners are generally less expensive than welding. But factors like design, hardware selection, durability, and functionality are all important considerations as well.
Choose the assembly method that works best for what your part needs-and of course let us know if you have any questions.
Post-Processing & Maintenance Implications
Choosing between welding and fastening isn’t just about assembly-it also impacts post-processing, maintenance, and long-term performance. Engineers should consider how each method affects surface finishing, repairability, and overall lifecycle costs.
Surface Finishing Considerations
- Welded Assemblies: Welding often requires grinding, sanding, and polishing to smooth out weld beads and create a seamless appearance. Additional finishing steps like powder coating, anodizing, or plating may be needed to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.
- Fastened Assemblies: Since fasteners don’t alter the base material, they typically require less post-processing. However, exposed fasteners may affect the aesthetic appeal or need secondary treatments like thread-locking adhesives, sealants, or corrosion-resistant coatings to improve longevity.
Maintenance & Repairability
- Welded Joints: Welding creates a permanent connection, making repairs more complex. If a component fails, the welded joint may need to be cut, ground down, and re-welded, which increases labor time and cost.
- Fastened Joints: Bolted or riveted assemblies allow for easier disassembly, making maintenance or part replacements more straightforward. This is particularly beneficial in applications that require frequent inspections, modifications, or upgrades.
Long-Term Performance & Wear Considerations
- Welded joints may experience heat distortion, residual stresses, or micro-cracking over time, which can weaken the structure-especially in applications subject to vibration or thermal cycling.
- Fasteners, while more flexible, can loosen over time due to vibration, requiring periodic re-torquing or thread-locking solutions. Preloading calculations and the use of lock washers or locking compounds can help mitigate this issue.
Ultimately, the choice between welding and fastening should take into account not just the initial fabrication process, but also post-processing complexity, long-term maintenance, and total lifecycle costs.
Sheet Metal Part Design for Manufacturing Tip
CORNERS AND WELDING
Proper technique on corners that need to be welded is necessary to reduce cost and increase the overall strength of the corners. Approved Sheet Metal will always reprogram corners that need to be welded to ensure customers receive the best possible welds.
Get more DFM TipsWelding Vs Fastening FAQ
What are the main assembly methods for sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication commonly involves two primary assembly methods: welding and fastening. Welding creates a permanent joint, while fasteners allow for disassembly and reassembly as needed.
When should I choose welding over fastening for my sheet metal fabrication project?
Welding is a suitable choice when you need a seamless and watertight joint, or when you want a clean, seamless appearance. It’s also ideal for parts that require exceptional strength and durability.
What are the advantages of using fasteners in sheet metal fabrication?
Fasteners provide the flexibility to disassemble and reassemble parts, making them suitable for applications where maintenance, repairs, or modifications may be required. They can also add strength and durability to thin or weak sheet metal components.
How do I decide between welding and fastening for my specific project?
Consider the specific use case:
- Welding is preferred for achieving a seamless appearance, watertight joints, and maximum strength.
- Fasteners are recommended for quick and easy fabrication, disassembly needs, and adding strength to weaker components.
Which assembly method is more cost-effective, welding, or fastening?
In general, fasteners tend to be less expensive than welding. However, cost should be weighed against factors such as design complexity, durability, and the specific functionality your part requires. It’s important to choose the method that best suits your project’s needs.