Last updated on May 19th, 2025 at 08:25 am
When it comes to protecting your metal parts, the choice of finish is crucial for both the functionality and aesthetics of the final product. At Approved Sheet Metal, we offer a variety of metal finishing options. Among these options, zinc plating stands out as a versatile and effective solution. In this post we will talk about what zinc plating is, common applications of zinc plating, and what type of zinc plating is right for your project.
Table of Contents
What is Zinc Plating?
Zinc plating is a process in which a thin layer of zinc is applied to the surface of a metal part. This is typically done through electroplating, where the metal part is submerged in a zinc-containing solution and an electric current is passed through, causing zinc to adhere to the part's surface.
The primary purpose of zinc plating is to provide corrosion resistance. Zinc acts as a sacrificial coating, corroding before the underlying metal does, thereby protecting it from rust and other forms of degradation.
Applications of Zinc Plating
Zinc plating is commonly used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, due to its cost-effectiveness and reliable performance. It is an excellent choice for parts that need to withstand harsh environments and maintain their integrity over time. Additionally, zinc plating can improve the appearance of metal parts, making them more attractive for customer-facing applications.
Zinc plating is often used with the following metals:
- Steel (Mild Steel/Carbon Steel): The most frequently zinc-plated sheet metal, steel benefits greatly from the corrosion resistance provided by zinc plating. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Stainless Steel: While stainless steel is already resistant to corrosion, zinc plating can provide an additional layer of protection in extremely harsh environments. However, this is less common due to the inherent corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
- Galvannealed Steel: This is a type of steel that is zinc-coated and then heat-treated to create a matte finish with enhanced paint adhesion.
- High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA): HSLA steel is used in structural applications where strength and weight are critical. Zinc plating can help protect this steel from corrosion without compromising its mechanical properties.
- Aluminum: Although aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, zinc plating can be used to enhance its corrosion resistance in particularly demanding environments. It is less common but can be found in certain aerospace and marine applications.
- Copper and Brass: Zinc plating can also be applied to copper and brass, primarily to improve their corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. These metals are often used in electrical components.
Type I vs. Type II Zinc Plating
When considering zinc plating for your metal parts, it is essential to understand the differences between Type I and Type II zinc plating. Both types offer the same basic corrosion-resistant properties, but they differ in appearance and the thickness of the zinc coating.
Type I Zinc Plating
Type I zinc plating is a basic form of zinc plating that provides corrosion resistance but does not offer a clean and polished finish. The etching process for Type I is not heavy enough to remove all particulates, grease, oils, and dust from the metal surface. As a result, parts plated with Type I zinc often look rough and dirty. This type of plating is usually sufficient for internal parts or components that are not visible to end users, where the primary concern is protection rather than appearance.
Type II Zinc Plating

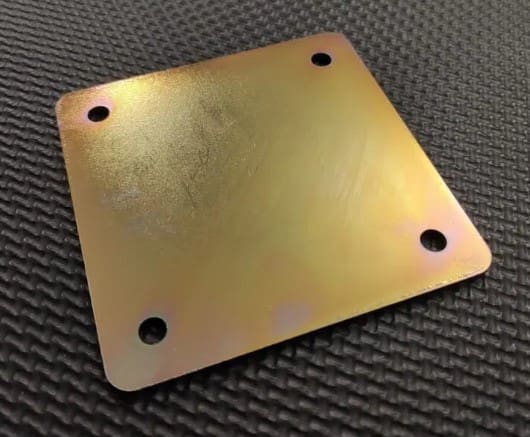
Type II zinc plating involves a much heavier etch, which fully removes the particulates, grease, oils, and dust from the metal surface and results in a thicker and more uniform zinc coating. This type of plating leaves a blue-tinged, shiny finish on the part, making it more aesthetically pleasing. The thicker coating also adds a bit of extra weight to the part, but this is generally negligible. Type II zinc plating is far more commonly requested than Type I due to its superior appearance and equally effective corrosion resistance.
Choosing the Right Zinc Plating Option for Your Needs
Both Type I and Type II zinc plating offer the same level of corrosion resistance, and at Approved Sheet Metal, we offer both Type I and Type II zinc plating for the same price. Ultimately, the choice between them should be based on the aesthetic and functional requirements of the part to be plated.
If the part will be visible to end users, Type II zinc plating is typically the better option due to its clean and shiny finish. For internal components where appearance is not a concern, or parts where the thickness of the finish must be minimized, Type I zinc plating may be the right choice.
We are committed to helping our customers select the best finishing options for their needs. When you provide us with detailed information about the intended use and environment of your parts, we can offer better guidance on the most suitable finishing option.
Choosing the right zinc plating from the start can save time, money, and ensure the longevity and appeal of your metal products. Reach out to us for expert advice and request a quote for high-quality zinc plating services tailored to your specific needs.